
Briefly, the extrarenal receptors primarily govern the activity of the sympathetic nervous system and natriuretic peptides. These receptors activate effectors that restore normovolemia by varying vascular resistance, cardiac output, and renal water and salt excretion. The change is sensed by the volume receptors, which are located in the cardiopulmonary circulation, the carotid sinuses and aortic arch, and in the kidney 2. The body responds to changes in effective circulating volume in two steps: 1. Sodium loading will tend to produce volume expansion, whereas sodium loss (e.g., due to vomiting, diarrhea, or drug management with diuretics) will lead to volume depletion. As a result, the regulation of extracellular fluid balance (by alterations in urinary sodium excretion) and the maintenance of the effective circulating volume are intimately related.

The effective circulating volume is biologically more relevant than the intravascular compartment and usually varies directly with the extracellular fluid volume. Capillary permeability is a further major mechanism that modulates the distribution of fluids across the capillary membrane.įull size image Effective circulating volumeĮffective circulating volume denotes the part of the intravascular compartment that is in the arterial system and is effectively perfusing the tissues. This force, which is called oncotic pressure, is due both to the concentration gradient of albumin (blood proteins other than albumin account for 50 percent of the weight of proteins in g in blood but only for 25 percent of the oncotic pressure) as well to the fact that albumin is anionic and therefore attracts cations (largely sodium) into the vascular compartment (Gibbs-Donnan effect figure 3). the higher concentration of proteins in the intravascular compartment as compared with that in interstitial fluid, which causes fluids to enter the vascular space. the hydrostatic pressure causes fluids to leave the vascular space, and b. Three major forces control the distribution of fluids across the capillary membrane (figure 2): a. The size of the intravascular compartment is determined by the overall size of the extracellular fluid compartment and by the Starling forces: they control the partition of fluids between intravascular and interstitial compartments across the capillary membrane that is crossed by salts like sodium chloride and by glucose but not by blood proteins (especially albumin). Finally, the transcellular fluid compartment comprises the digestive, cerebrospinal, intraocular, pleural, peritoneal and synovial fluids but will not be further addressed in this review. The extracellular compartment is further subdivided into the interstitial and the intravascular compartments (blood volume), which contain two-thirds and one-third of the extracellular fluid, respectively. Consequently potassium largely determines the intracellular and sodium the extracellular compartment. The solute composition of the intracellular and extracellular fluid differs considerably because the sodium pump maintains potassium in a primarily intracellular and sodium in a primarily extracellular location. The intracellular compartment contains about two-third of the total body water and the remaining is held in the extracellular compartment. after puberty males generally have 2 to 10 percent higher water content than females (figure 1). the water content of a newborn, an adolescent and an elderly man are approximately 75, 60 and 50 percent b. The most important determinants of the wide range in water content are age and gender: a. For each sample of blood obtained after infusion of the labeled RBCs, radioactivity per mL of blood was calculated and was plotted versus time.Water makes up 50-75 percent of the body mass. › NCBI › Literature › PubMed Central (PMC) by DM Mock - 2008 - Cited by 11 - Related articles RCV determination by (14C)cyanate, 51Cr, and (125I)streptavidin.
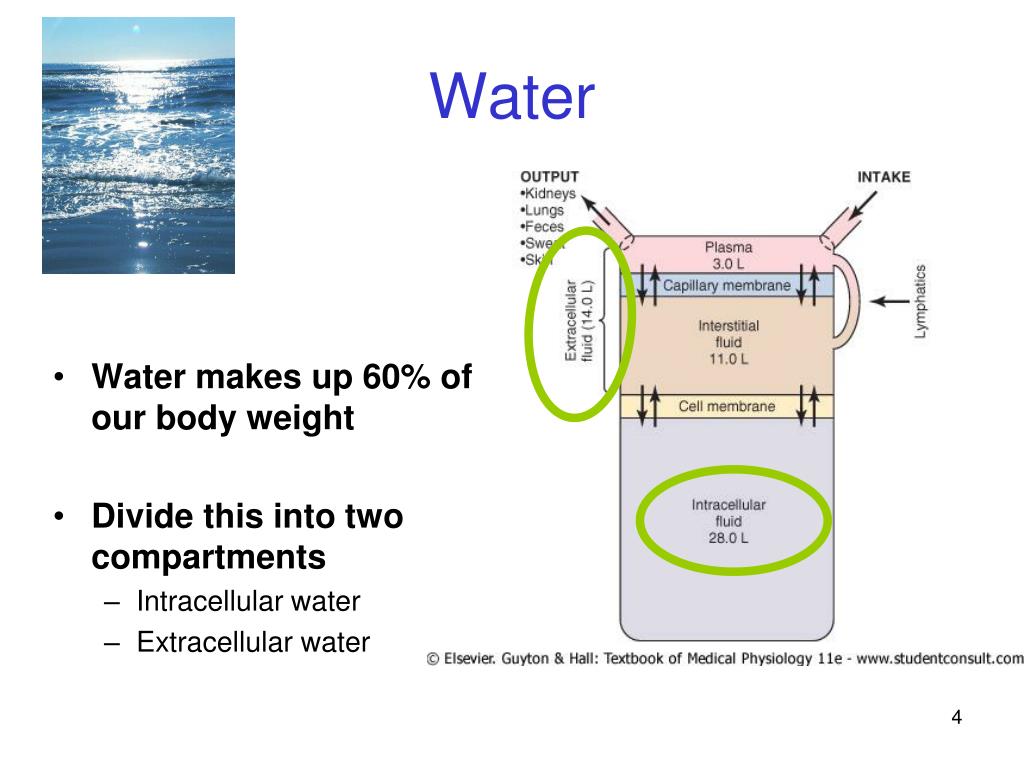


Infants are more vulnerable for water loss due to: Ion ICF (mmol/L of H20) ECF(mmol/L of H20)ĭeuterium oxide/heavy water, Tritium oxide, Aminopyrine − Ions like Na+,Ca2+,K+,Cl-, etc affects


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
